About Hosier
CATEGORIES OF HOSIERY
Hosiery is considered as one of the accessories of clothing. It protects people's feet and legs, keeps them warm and healthy, and makes them look beautiful. It is mainly divided into two categories:
一、Socks: including toe socks, slipper socks, bootie socks, etc.
二、Pantyhose: including pantyhose, footless tights, tights and body stockings.
Furthermore, it can also be classified in different ways as follows:
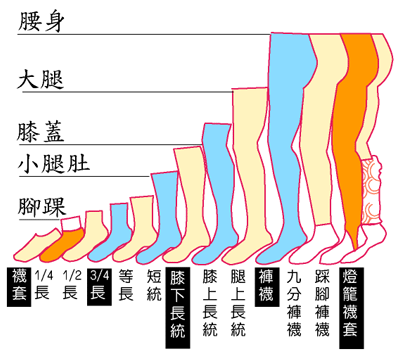
| CLASSIFIED BY | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Materials | ylon stockings,elastic panty hose,cotton socks, wool socks,acrylic socks,functional fiber socks,and all kinds of T/C socks |
| Construction | Plain or with patterns |
| Styles | Low-Cut-Pad,trainer Liner,ankle,mid-calf,knee high,above-the knee,thigh high,pantyhose,footless tights,tights,leg warmer,b ody stockings…. |
| CLASSIFIED BY | For sport, leisure, leg protection, eurhythmics, fashion, keeping warm, medical, and health |
| Wearers | Baby,kids,student's socks,teenagers',men's and women's |
MANUFACTURING PROCESS
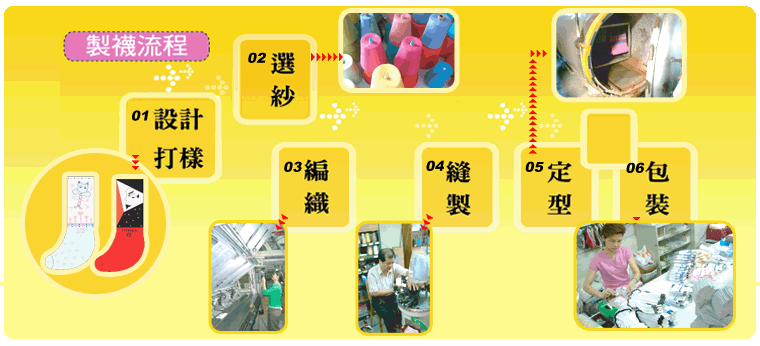
Different materials and machines are used to make different kinds of hosiery. However, generally speaking, their manufacturing process is very similar. First, after the designs and production samples are finalized, the proportion of the ingredients of the raw materials is determined. Next, the knitting machines produce the half-finished products (also called hose ). Then, the tiptoes and heels are stitched and trimmed (adding gusset is a necessary procedure for pantyhose).Following comes the embroidering and dyeing before they are pressed and boarded at a high temperature. Packaging is the last procedure.Take socks for example, its manufacturing process is as follows:
We can see clearly from viewing the above manufacturing process that machines are used only for knitting. Manual labor is still needed at the other stages of the manufacturing process, especially for sewing and packaging which require for a lot of manual labor. Concluding from it, hosiery industry relies on multiple labor process and inclines to be an intensive labor industry.
TYPES OF HOSIERY PRODUCTION
The production is completed mainly under a sub-contract system. About 90% of the manufacturers produce hosiery products in cooperation with their sub-contractors. Three parties are involved in the hosiery production, they are:

Principal
he hosiery manufacturers who sell their products directly to wholesalers and trading companies.
Contractors
The factories that do the following jobs for the principals under contracts: production by machines, sewing , pressing and boarding, dyeing, and packaging.

In-house sub-contractor
The sub-contractors finish the jobs at home, mainly for sewin g and packaging.
HISTORY AND EVOLUTION OF KNITTING MACHINES

Manual knitting machine used in early stages: They had been put in stock or weeded out.

Semi-automatic knitting machines: Only a few of them are still running.
Semi-automatic knitting machines used between 1960 and 1970: Most of them had been put in stock.
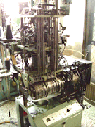
Jacquard knitting machines imported from Daito Co., Ltd., Japan between 1960 and 1970: models varied from stitch counts in the cylinders as Model 96, 132, 144, 176, 200, and 216.

DERA knitting machine made .in the Czech Republic : They had run for thirty to forty years.

Computerized jacquard knitting machines: They increase the daily output and save labor hours and labor.
| Years | Major knitting machine models | Output | Improvement | Affect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
301930-1940 |
Manual operation | 1 machine/operator, 3-5 dz/10 hr/day for adults' socks | An intensive labor industry was formed | |
| Semi-automatic, non- jacquard | About the same as the manual machines',1 machine/one operator | Operated by motor | Less labor required only | |
501950-1960 |
Semi-automatic jacquard | Simple patterns are available on hosiery | With jacquard attachment on cams | |
| Automatic, non- jacquard | 6-8 pairs of adult socks/hr,10 machines/operator | Automatic reversible cams, forming heels automatically | Labor economic,manual machines were weeded out gradually | |
| Automatic 25-step jacquard | More complicated patterns available, 4-10machines/operator | The control of jacquard was strengthened. | Export started in 1964. Since then, the business flourished. The products were mainly made by machines. | |
701970 |
Automatic computerized | Same as the automatic jacquard's, but20 machines/operator | Automatic cutting, stitching, with programs for pattern designing | Much less labor is needed while more computer skills are required. |
801980 |
Non-cylinder computerized (fully computerization) | The cams and lever are directly controlled by computer programs and server motors | The machines consume slowly; therefore, they need less maintenance and repairs but rely more on electronic components |
Sources: Pao-ling Liu (2000) 《 THE CHANGES OF THE MANUFACTURING SYSTEM OF HOSIERY KNITTING INDUSTRY AND THE SPACE CONSTRUCTION IN SHE-TOU 》
